Whoever the Most High is a witness for Truth, he need not claim it. The claim is a sign of his veiling from Truth and Peace.
A quote from dhū al-nūn from al-Sha’rānī, ’Abd al-Wahhāb. Lawāqiḥ Al-Anwār al-Qudusīyya Fī Manāqib al-ʿUlamā Wa al-Ṣūfīyya. Maktabat al-Thaqāfa al-Dīnīyya, 2005, p. 129.
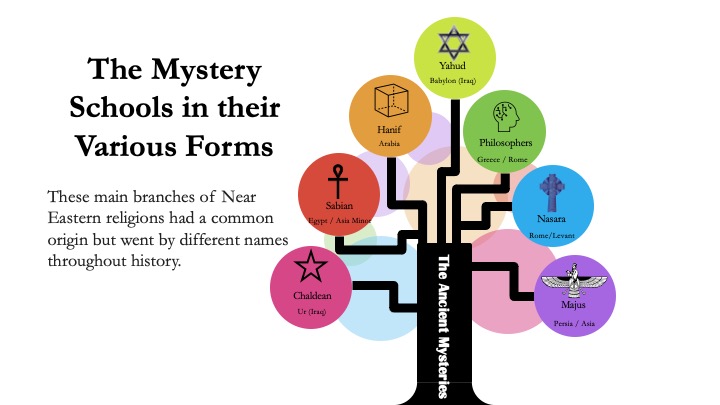
In recent years, the Moorish Science Temple (MST) has become one of the many groups on the conscious chit’lin circuit; some of them Hanifs, most of them Sabians. Unfortunately, the unscrupulous reader might mistake the Sabians among them for Muslims or, even worse, a factual representation of history. As a Muslim researcher with a specialization in the Arabic language and Islamic history, it is my responsibility to debunk the bogus claims propagated by such groups.
In one recent YouTube presentation on TITANS TV, a Moorish Science researcher and self-proclaimed Arabic teacher by the name of Kemetian Adept Hieruphant attempted to advocate for his Sabian-inspired MST doctrine using George G. M. James’ Stolen Legacy, orientalist mythology about the Egyptian Sufi, Dhū al-Nūn (more on this in another post), and a hodgepodge of information to confuse you. I beseech the reader not to confuse claims to knowledge for actual knowledge, as was the message of Dhū al-Nūn. In this post, I will focus on deconstructing Kemetian’s treatment of Stolen Legacy and the history of the Moors.
While Kemetian uncritically accepts James’ thesis, he provides little to no detail to demonstrate the MST position. Kemetian throws a lot of images and texts at you, but his attempt to connect the so-called Moors to the ancient Egyptians is weak because it has no basis in the actual history of North Africa or the Islamic world. He, like many so-called conscious folk, suffers from debilitating confirmation bias; believing his point of view is the only way of seeing the information. Why does he perpetuate a bogus conspiracy theory about the death of James? (A past professor of mine researched and debunked this claim) Why does he think that by virtue of genetic lineage he has a rightful claim to the knowledge of ancient Kemet without actually studying it? And what is a mystery school today other than a university? Kemetian’s misinformation not only reduces his credibility but also the credibility of anyone who takes this topic seriously.
George GM James’ Misunderstood Stolen Legacy
Kemetian introduces his presentation with the passage from Stolen Legacy that opens Islam and the Ancient Mysteries Vol. 1. In my book, I put forth a better way to understand James’ thesis, which lies in answering three main questions:
- Who were the Moors discussed by James.
- What knowledge did the ancient Egyptians possess?
- How did the Moors acquire ancient Egyptian knowledge?
First, the Moors of history were not followers of Noble Drew Ali or members of an organization called the Moorish Science Temple. “Moor” was an epithet used by Europeans during the Middle Ages to refer to people with dark features and Muslims in general, and North African Muslims specifically. Whatever its original meaning, it was lost on European people by the Middle Ages. They were not calling North African Muslims “gods” or anything of that nature.
If we take the European usage of Moor at face value, it means someone who is dark (relative to the average European phenotype) and/or from North Africa and/or Muslim. This is a broad span of people, which can encompass SubSaharans, Berbers, Arabs, Persians, and Indians and often times it has referred to Jews, Christians, and Muslims living in Muslim-controlled lands.

Secondly, we must have an understanding of what knowledge was attributed to the ancient Egyptians. While James touches on this, he is not completely clear as to what that knowledge was. On the one hand, James characterizes this ancient knowledge as a secret, exclusively for Egyptians, transmitted orally from teacher to student, and forbidden to be written down. On the other hand, he writes that this knowledge was kept in books at temples and libraries, which were eventually copied and plagiarized by the Greeks (particularly Aristotle), and then they became the domain of the Greeks, Freemasons, Theosophists, and occultists. How James deduces this can be challenged on the grounds that he retrofits the concepts of contemporary esoteric movements on to ancient Egyptian Mystery Schools. This is only James’ speculation, not concrete proof.
Additionally, James reconstructs the ancient Egyptian curriculum using a mixture of Christian and pre-Christian Greek sources, whose works he sees to be untrustworthy since the pre-Christian Greeks allegedly stole knowledge from the Egyptian Mysteries and the Christians attempted to annihilate them. Nevertheless, the curriculum according to James was made up of the seven liberal arts, secret languages and mathematical symbolism, as well as magic. This included memorizing the books of Hermes that teach the hieroglyphs, cosmography, geography, astronomy, typography, how to slaughter animals, law, theology, medicine, among other subjects.
Many of these subjects where known and practiced all over the ancient world including ancient Babylon and India, as James alludes to, as well as in Europe and the Americas. There simply is no concrete proof that this curriculum originated in Egypt, no matter how much we want to believe it. In one aspect, it was a secret that died with the last Egyptian priest. Any other empirical knowledge they developed could also be reconstructed by other people with similar aims. Not only that, but both the Islamic civilization and later the current European civilization surpassed the ancient Egyptians in the empirical sciences (no matter what our criticisms of those civilizations are). It is also much more logical and backed by evidence to think that the world’s knowledge was an intergenerational, multi-ethnic collective effort rather than the work of one people.
Finally, how did ancient knowledge transfer to the the hands of the so-called Moors and then to Western Europe? I demonstrate this process in Islam and the Ancient Mysteries Vol. 1. I firmly demonstrate that Muslim civilization under the Hanif creed absorbed the knowledge of ancient Near East, serving as a bridge between the ancient and modern world. The following is a summary of this history.
The True History of the Moors
What’s lost on Kemetian and the Moors are the key players in history that represented this passage of knowledge. If we were to question MST folk to name some of the Moors who conveyed knowledge from the ancient Mysteries, they would be hard pressed to name one. Yet, I have researched several of them for my book: the Ḥarrānian Thābit ibn Qurrah, the Persian family Āli Nawbakht, the Abbasid Translation Movement, and particular Muslim philosophers like Ibn Sina, al-Ghazali, and Ibn Rushd and their respective philosophical positions. There are countless more that historians have researched.
A synopsis of this history starts with the decline of the Mysteries, prior to Christianity. In the Greco-Persian wars, Alexander massacred Iran and sought to extinguish the Persian-Babylonian Mysteries and the knowledge they acquired. He brought their manuscripts to current-day Egypt and had them translated into Greek and Coptic and destroyed the Persian originals. The Greeks were therefore consolidating the knowledge of ancient Egypt and Babylon. As of the 4th and 3rd centuries BCE, this knowledge was most readily available in Greek and Coptic (an advanced form of the ancient Egyptian language).
Christianity was a Hanif system that challenged the Sabianism that proliferated among Judaism and the so-called Philosophers. The disciples spread the monotheistic message of Jesus, which eventually became mixed with the ideas of gnostics (i.e. Sabians), such as Simon Magus, Menander, and yes, Paul. The early scholars of Christianity were educated in the schools of the Greeks and were able to argue the Sabians in their own terms. Though the Christians opposed the Sabians, they ended up absorbing much of the ancient knowledge in the Eastern Church, which split from the Western Church relatively early in the history of Christiandom.
In the meanwhile, the Persians sought to reconstruct their mysteries by reviving the manuscripts found at the extremities of the Persian empire near India and China. They were open to various sects of Christianity such as the Nestorians. Many of those Christians preserved ancient knowledge they inherited from the Greeks in the Syriac language. By the time the Muslims conquered, these works began to be translated into Arabic. This proliferated during the Abbasid Caliphate that funded the Translation Movement; translating the works of the ancient mysteries primarily from Greek, Syriac, and Persian, because knowledge from the ancient world was largely consolidated in these languages.
While the likes of Thābit ibn Qurrah, the Nawbakht family, and Ibn Muqaffaʿ played key roles in this Translation Movement, the effort cannot be attributed to one tribe, ethnic group, race, or religion. Thābit’s ethnicity cannot be ascertained although he was a native Syriac speaker and also spoke Greek and Arabic. The Nawbakht family were from a lineage of Persian Magians who specialized in astrology. Likewise, Ibn Muqaffaʿ was a Persian litterateur responsible for translating numerous books from the Persian and Indian literary heritage. Muslim and Arabic-speaking scholars of other faiths engaged these works for nearly a millennium, including the questionable works on astrology and magic. Yet, the most controversial issues centered on the philosophical concepts of the creation of the universe, pantheism, and the like, which I covered in the post Is God the Universe?
Social media scholars from the MST and other so-called conscious groups cannot accurately describe how or why this passed from Muslim lands to Western Europe. The Christian Crusades against Muslims began in the 11th century, at the height of the Translation Movement. One should also observe that during this time, many Europeans were “orientalists,” meaning that they admired Arabic language, culture, and knowledge; see (Burnett, 2008, p. 22). Many in Western Europe, who have long since been cut off from the ancient Greeks, rediscovered the knowledge compiled in Greek through Arabic. As political enmity grew between Western European Christiandom and Islamdom, the intellectual affinity grew. One might notice that some of the most erudite scholars from Andalus, migrated to Egypt during the Inquisitions such as al-Qurṭubī and Abū Ḥayyān al-Andalusī, etc. Khaled El-Rouayheb performed an excellent study on the influence of Maghribī scholars on theology and logic in Ottoman-controlled Egypt and prior. Many of whom were from the Ṣanhajah Berber ethnic group.
No narrative about the Moors’ passage of knowledge to Europe would be complete without mentioning the 12th century CE polymath Ibn Rushd (the grandson). In addition to being from a scholarly lineage based in Córdoba, he was a jurist, physician, and Aristotelian philosopher. In fact, he was known as the chief commentator on the works attributed to Aristotle. The untrained reader must remember that Aristotelian philosophy was at the core of Sabian doctrine, which was a proponent of the eternity of the universe. Ibn Rushd wrote a vehement defense of philosophy and Aristotelian concepts in his Faṣl al-Maqāl and Tahāfut al-Tahāfut against Abū Ḥāmid al-Ghazālī’s Tahāfut al-Filāsifah. Although Ibn Rushd’s positions were rejected by most Muslim scholars, many European orientalists were enamored with his works. This even prompted the Christian theologian, Thomas Aquinas to write a response opposing the eternity of the universe.
Conclusion
The perspectives propagated by the Sabian factions of the MST amounts to nothing short of pseudoscience and a creative re-telling of history. Only simpletons are impressed. History does not begin with the interpretations of pseudo-scholars, but the collective evidence established by a body of researchers. Unfortunately, the MST lacks members who have advanced through the degrees of scholarship: sufficient tertiary education, specializations, peer-reviewed publications, academic integrity and humility, etc. Furthermore, there is nothing novel about their teachings. Their teachings are simply Sabian-Noir doctrines; the same doctrines that have confused our people for generations. In another post, I will unravel some of their doctrines and their erroneous characterizations of Sufism.